Have you ever wondered how your favorite streaming platform always seems to know what you want to watch next? Or how your email filters spam with surprising accuracy?
That’s machine learning (ML) at work—an exciting branch of artificial intelligence that’s shaping our digital lives every day.
In this guide, we’ll explore what machine learning really means, its core types, how it works, and where you see it in action. Whether you’re a beginner or simply curious, this breakdown will give you the clarity you need.
What Is Machine Learning?
Machine learning is a type of artificial intelligence (AI) that enables computers to learn from data and improve their performance over time without being explicitly programmed for every task.
Think of it as teaching computers to recognize patterns and make decisions, much like training a dog to fetch a ball. With enough examples (data), the system learns to predict and act correctly.
In short, machine learning turns data into decisions.
Machine Learning vs. Traditional Programming
To understand ML better, it helps to compare it with traditional programming.
-
Traditional programming: Developers write explicit rules (if X, then Y).
-
Machine learning: The system is trained with past data, allowing it to recognize patterns and adapt without predefined rules.
For example, instead of coding rules for spam detection, ML models analyze thousands of labeled emails (“spam” vs. “not spam”) and learn the difference on their own.
The outcome? Smarter, more adaptable systems.
The Three Main Types of Machine Learning
Machine learning isn’t one-size-fits-all. It comes in three major categories, each serving different purposes.
1. Supervised Learning
Supervised learning relies on labeled data, meaning the system learns from examples with known outcomes.
Examples include:
-
Email spam detection
-
Predicting house prices
-
Facial recognition
Think of it like flashcards: the system studies the answers and learns to predict new ones.
2. Unsupervised Learning
Here, the system works with unlabeled data and discovers hidden patterns or groupings on its own.
Applications include:
-
Customer segmentation
-
Market basket analysis (“people who bought this also bought…”)
-
Fraud detection
It’s like giving the computer a puzzle with no instructions and letting it find patterns independently.
3. Reinforcement Learning
Reinforcement learning uses trial and error to teach models. The system learns by taking actions, receiving rewards for correct moves, and penalties for mistakes.
Examples include:
-
Game AI (e.g., Google’s AlphaGo)
-
Robotics
-
Self-driving cars
Think of it as teaching a puppy tricks with treats and corrections.
How Does Machine Learning Work?
While the process can get technical, here’s a simplified step-by-step look at how machine learning operates:
-
Collect Data – Gather large sets of relevant information.
-
Prepare Data – Clean, organize, and (if needed) label it.
-
Choose a Model – Select the right algorithm for the problem.
-
Train the Model – Feed the system with data so it can learn.
-
Test the Model – Check performance on new, unseen data.
-
Refine the Model – Adjust and improve accuracy.
-
Deploy – Use the trained model in real-world applications.
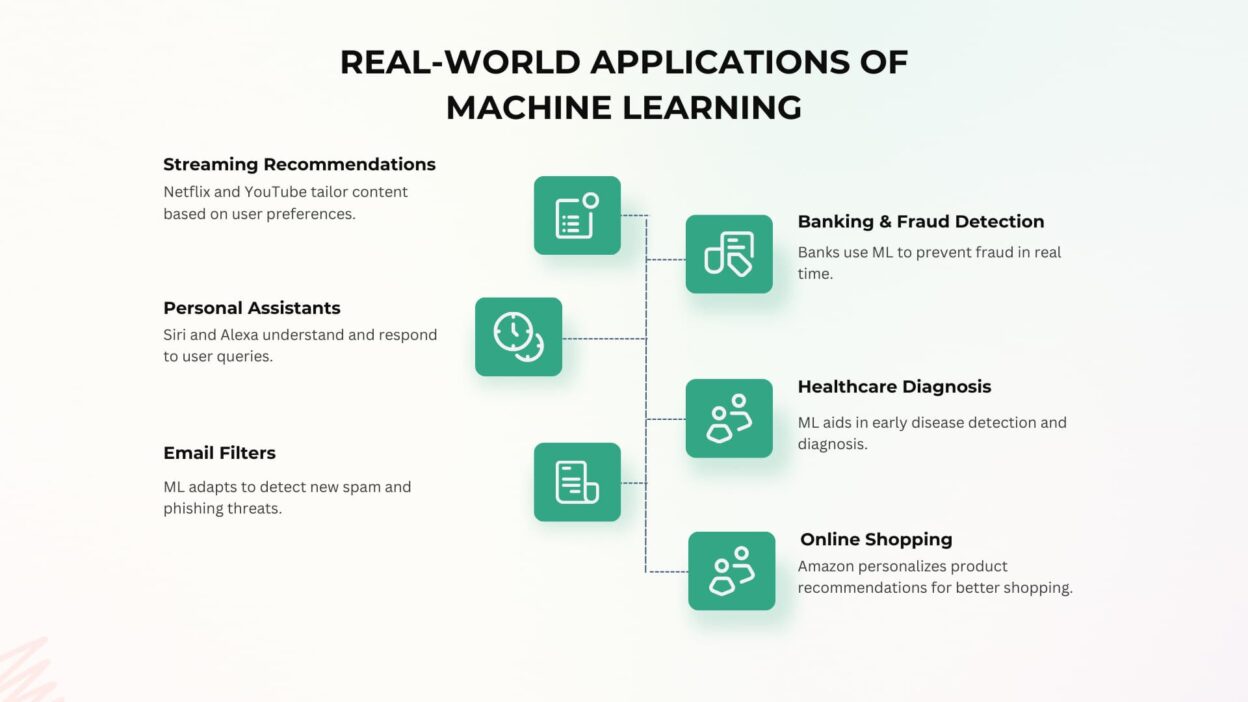
Real-World Applications of Machine Learning
Machine learning isn’t just for tech companies—it’s already woven into everyday life. Here are some familiar examples:
1. Streaming Recommendations
Platforms like Netflix and YouTube analyze your watch history and behavior to suggest shows and videos tailored to your taste.
2. Personal Assistants
Voice-powered assistants like Siri, Alexa, and Google Assistant use ML-driven natural language processing to understand and respond to queries.
3. Email Filters
Spam detection tools use ML to constantly adapt, spotting new threats like phishing and junk mail.
4. Banking & Fraud Detection
Banks rely on ML to detect unusual transactions and prevent fraud—often in real time.
5. Healthcare Diagnosis
Medical imaging tools use ML to detect early signs of diseases, helping doctors make faster, more accurate diagnoses.
6. Online Shopping
E-commerce platforms like Amazon use ML to personalize product recommendations and improve customer experience.
Final Thoughts
Machine learning is no longer just a buzzword—it’s a core driver of innovation across industries. From powering personal assistants to improving healthcare and finance, ML is helping create smarter, more efficient systems.
And the best part? This is just the beginning. As data grows and algorithms evolve, machine learning will continue shaping the future of work, business, and everyday life.