Discover the best backend frameworks for building scalable web apps in 2025. Explore top choices like Node.js, Django, and more, with detailed insights, use cases, and tips to select the ideal framework for your project.
Introduction
Choosing the right backend framework is crucial for building scalable, efficient, and maintainable web applications. In 2025, as web apps demand higher performance and flexibility, understanding the best backend frameworks available becomes essential for developers, startups, and enterprises alike. This blog post explores the top 10 backend frameworks that excel in scalable web architecture, highlights key backend development tools, and compares popular technologies like Node.js vs Django to help you make informed decisions.
Understanding Backend Frameworks and Scalable Web Architecture
Backend frameworks provide the foundation to develop server-side logic, database interactions, user authentication, and application routing. They streamline backend development by offering pre-built components, patterns, and security features. A scalable web architecture ensures your app can handle increasing traffic and data growth efficiently without compromising performance. Selecting a robust backend framework is imperative to achieve scalability through modular code, asynchronous processing, and seamless integration with other services.
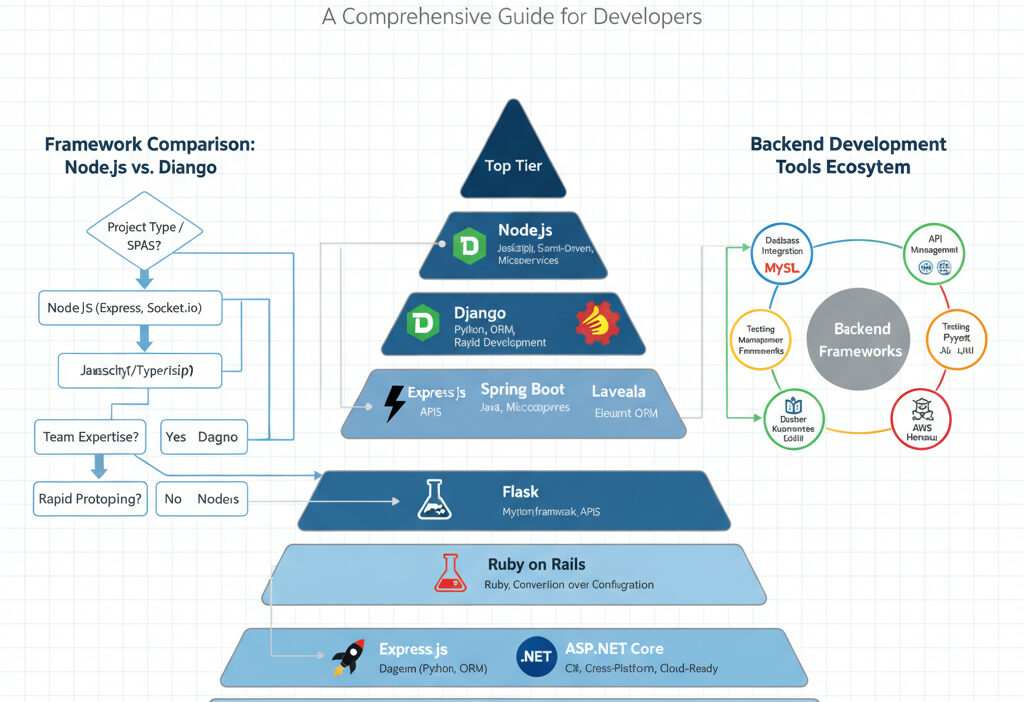
Top 10 Best Backend Frameworks in 2025
1. Node.js (Express.js)
Overview: Node.js is a runtime environment enabling JavaScript on the server. Express.js is one of the most popular minimalistic frameworks built on Node.js.
Use Cases: Real-time applications, APIs, microservices, single-page apps.
Pros: Non-blocking I/O, large community, rich npm ecosystem, fast development cycle.
Cons: Callback complexity, less opinionated architecture.
Notable Users: Netflix, LinkedIn, PayPal.
2. Django
Overview: A high-level Python framework emphasizing rapid development and pragmatic design.
Use Cases: Content management systems, scientific computing platforms, social networks.
Pros: Batteries-included, security features, ORM, admin panel.
Cons: Monolithic, steeper learning curve for beginners.
Notable Users: Instagram, Disqus, Mozilla.
3. Ruby on Rails
Overview: A convention-over-configuration framework written in Ruby.
Use Cases: E-commerce platforms, startups, social platforms.
Pros: Developer-friendly, strong community, rich libraries.
Cons: Performance bottlenecks at scale, runtime speed.
Notable Users: GitHub, Airbnb, Shopify.
4. Spring Boot (Java)
Overview: A Java-based framework aimed at simplifying production-ready applications.
Use Cases: Enterprise applications, microservices, large systems.
Pros: Robust, scalable, extensive documentation, security.
Cons: Verbose configuration, higher entry complexity.
Notable Users: Netflix, Amazon, LinkedIn.
5. Flask (Python)
Overview: A microframework that provides simplicity and flexibility.
Use Cases: Prototyping, small to medium apps, RESTful APIs.
Pros: Lightweight, easy to learn, extensible.
Cons: Lesser built-in features, requires extensions.
Notable Users: Pinterest, LinkedIn.
6. Laravel (PHP)
Overview: PHP framework focused on elegant syntax and powerful features.
Use Cases: Web apps, CMS, e-commerce sites.
Pros: MVC architecture, ORM, huge ecosystem.
Cons: Performance limitations at scale relative to other languages.
Notable Users: BBC, 9GAG.
7. ASP.NET Core
Overview: Microsoft’s cross-platform, high-performance framework.
Use Cases: Enterprise applications, cloud services, APIs.
Pros: High performance, mature tooling, security.
Cons: Windows-centric perception, steeper learning curve.
Notable Users: Stack Overflow, Microsoft, Taco Bell.
8. Phoenix (Elixir)
Overview: Real-time apps with high concurrency using Elixir’s BEAM VM.
Use Cases: Chat apps, analytics dashboards, IoT.
Pros: Fault-tolerant, scalable, real-time capabilities.
Cons: Smaller community, less mainstream.
Notable Users: Bleacher Report, Pinterest (some parts).
9. Koa.js
Overview: Lightweight Node.js framework designed by Express creators.
Use Cases: APIs, web apps requiring middleware flexibility.
Pros: Modern async/await support, minimal footprint.
Cons: Smaller community than Express.
Notable Users: IBM, Accenture.
10. CodeIgniter (PHP)
Overview: A lightweight PHP framework with minimal footprint.
Use Cases: Small projects, rapid development.
Pros: Easy to install, fast performance.
Cons: Limited built-in features.
Notable Users: The Mail & Guardian.
Node.js vs Django: A Quick Comparison
Node.js with Express.js offers asynchronous, event-driven architecture ideal for real-time applications, while Django provides a full-featured, synchronous framework with strong built-in security and admin options. Your choice depends on language preference (JavaScript vs Python), application complexity, and scalability needs.
Tips for Choosing the Best Backend Framework
- Project Requirements: Consider app type, expected traffic, and complexity.
- Language Expertise: Choose a framework aligned with your team’s skillset.
- Community and Support: Larger communities offer better resources and libraries.
- Performance Needs: Evaluate synchronous vs asynchronous capabilities.
- Scalability: Ensure the framework supports modular growth and load balancing.
- Development Speed: Frameworks with rich tools and conventions can speed up time-to-market.
Conclusion
Finding the best backend frameworks for scalable web apps hinges on understanding your project’s needs, team capabilities, and long-term goals. Frameworks like Node.js, Django, and Spring Boot lead the pack by offering diverse strengths based on scalability, performance, and community support. Whether you’re building a lightweight API or an enterprise-grade application, selecting the right backend toolset will empower your scalable web architecture and accelerate development in 2025 and beyond.
Introduction
Choosing the right backend framework is crucial for building scalable, efficient, and maintainable web applications. In 2025, as web apps demand higher performance and flexibility, understanding the best backend frameworks available becomes essential for developers, startups, and enterprises alike. This blog post explores the top 10 backend frameworks that excel in scalable web architecture, highlights key backend development tools, and compares popular technologies like Node.js vs Django to help you make informed decisions.
Understanding Backend Frameworks and Scalable Web Architecture
Backend frameworks provide the foundation to develop server-side logic, database interactions, user authentication, and application routing. They streamline backend development by offering pre-built components, patterns, and security features. A scalable web architecture ensures your app can handle increasing traffic and data growth efficiently without compromising performance. Selecting a robust backend framework is imperative to achieve scalability through modular code, asynchronous processing, and seamless integration with other services.
Top 10 Best Backend Frameworks in 2025
1. Node.js (Express.js): Overview: Node.js is a runtime environment enabling JavaScript on the server. Express.js is one of the most popular minimalistic frameworks built on Node.js.
Use Cases: Real-time applications, APIs, microservices, single-page apps.
Pros: Non-blocking I/O, large community, rich npm ecosystem, fast development cycle.
Cons: Callback complexity, less opinionated architecture.
Notable Users: Netflix, LinkedIn, PayPal.
2. Django: Overview: A high-level Python framework emphasizing rapid development and pragmatic design.
Use Cases: Content management systems, scientific computing platforms, social networks.
Pros: Batteries-included, security features, ORM, admin panel.
Cons: Monolithic, steeper learning curve for beginners.
Notable Users: Instagram, Disqus, Mozilla.
3. Ruby on Rails: Overview: A convention-over-configuration framework written in Ruby.
Use Cases: E-commerce platforms, startups, social platforms.
Pros: Developer-friendly, strong community, rich libraries.
Cons: Performance bottlenecks at scale, runtime speed.
Notable Users: GitHub, Airbnb, Shopify.
4. Spring Boot (Java): Overview: A Java-based framework aimed at simplifying production-ready applications.
Use Cases: Enterprise applications, microservices, large systems.
Pros: Robust, scalable, extensive documentation, security.
Cons: Verbose configuration, higher entry complexity.
Notable Users: Netflix, Amazon, LinkedIn.
5. Flask (Python): Overview: A microframework that provides simplicity and flexibility.
Use Cases: Prototyping, small to medium apps, RESTful APIs.
Pros: Lightweight, easy to learn, extensible.
Cons: Lesser built-in features, requires extensions.
Notable Users: Pinterest, LinkedIn.
6. Laravel (PHP): Overview: PHP framework focused on elegant syntax and powerful features.
Use Cases: Web apps, CMS, e-commerce sites.
Pros: MVC architecture, ORM, huge ecosystem.
Cons: Performance limitations at scale relative to other languages.
Notable Users: BBC, 9GAG.
7. ASP.NET Core: Overview: Microsoft’s cross-platform, high-performance framework.
Use Cases: Enterprise applications, cloud services, APIs.
Pros: High performance, mature tooling, security.
Cons: Windows-centric perception, steeper learning curve.
Notable Users: Stack Overflow, Microsoft, Taco Bell.
8. Phoenix (Elixir): Overview: Real-time apps with high concurrency using Elixir’s BEAM VM.
Use Cases: Chat apps, analytics dashboards, IoT.
Pros: Fault-tolerant, scalable, real-time capabilities.
Cons: Smaller community, less mainstream.
Notable Users: Bleacher Report, Pinterest (some parts).
9. Koa.js: Overview: Lightweight Node.js framework designed by Express creators.
Use Cases: APIs, web apps requiring middleware flexibility.
Pros: Modern async/await support, minimal footprint.
Cons: Smaller community than Express.
Notable Users: IBM, Accenture.
10. CodeIgniter (PHP): Overview: A lightweight PHP framework with minimal footprint.
Use Cases: Small projects, rapid development.
Pros: Easy to install, fast performance.
Cons: Limited built-in features.
Notable Users: The Mail & Guardian.
Node.js vs Django: A Quick Comparison
Node.js with Express.js offers asynchronous, event-driven architecture ideal for real-time applications, while Django provides a full-featured, synchronous framework with strong built-in security and admin options. Your choice depends on language preference (JavaScript vs Python), application complexity, and scalability needs.
Tips for Choosing the Best Backend Framework
- Project Requirements: Consider app type, expected traffic, and complexity.
- Language Expertise: Choose a framework aligned with your team’s skillset.
- Community and Support: Larger communities offer better resources and libraries.
- Performance Needs: Evaluate synchronous vs asynchronous capabilities.
- Scalability: Ensure the framework supports modular growth and load balancing.
- Development Speed: Frameworks with rich tools and conventions can speed up time-to-market.
Conclusion
Finding the best backend frameworks for scalable web apps hinges on understanding your project’s needs, team capabilities, and long-term goals. Frameworks like Node.js, Django, and Spring Boot lead the pack by offering diverse strengths based on scalability, performance, and community support. Whether you’re building a lightweight API or an enterprise-grade application, selecting the right backend toolset will empower your scalable web architecture and accelerate development in 2025 and beyond.