React has consistently pushed the boundaries of frontend development, and in 2025, React Server Components (RSCs) are no longer experimental—they’re becoming a mainstream solution for building highly performant, scalable applications. For developers navigating modern web architecture, understanding how RSCs work and why they matter is essential.
In this article, we’ll explore React Server Components, their differences from traditional rendering methods, and their impact on the future of React applications.
What Are React Server Components (RSCs)?
React Server Components are a new feature that allows developers to render components entirely on the server and stream the result to the client. Unlike client components, which ship JavaScript to the browser for execution, RSCs deliver pre-rendered UI without sending unnecessary JavaScript bundles.
In simpler terms:
- Client Components = run in the browser, include JS bundles.
- Server Components = run on the server, send rendered output, no JS sent to client.
This makes RSCs extremely efficient because they reduce bundle size and optimize data fetching.
Why React Server Components Matter in 2025
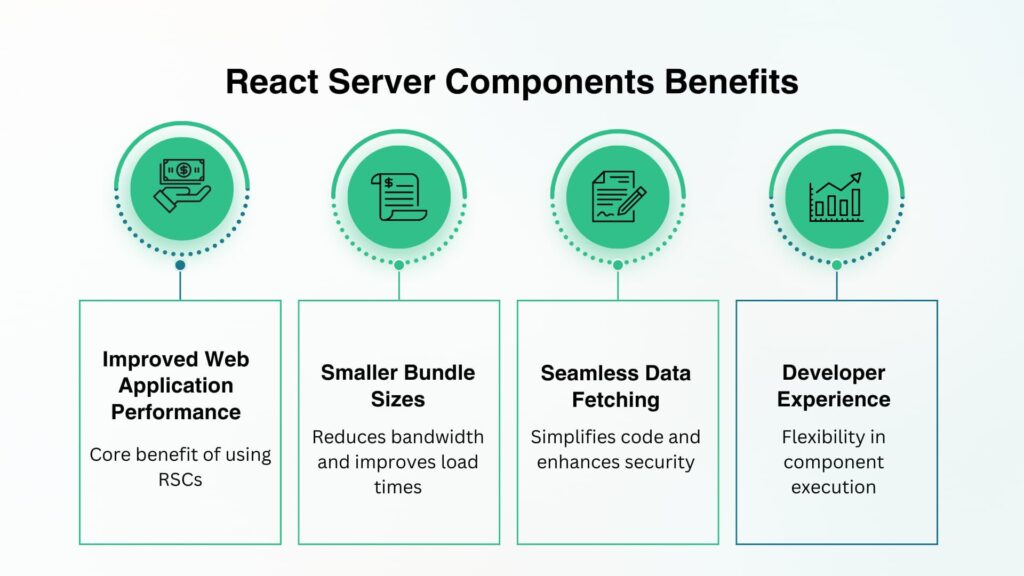
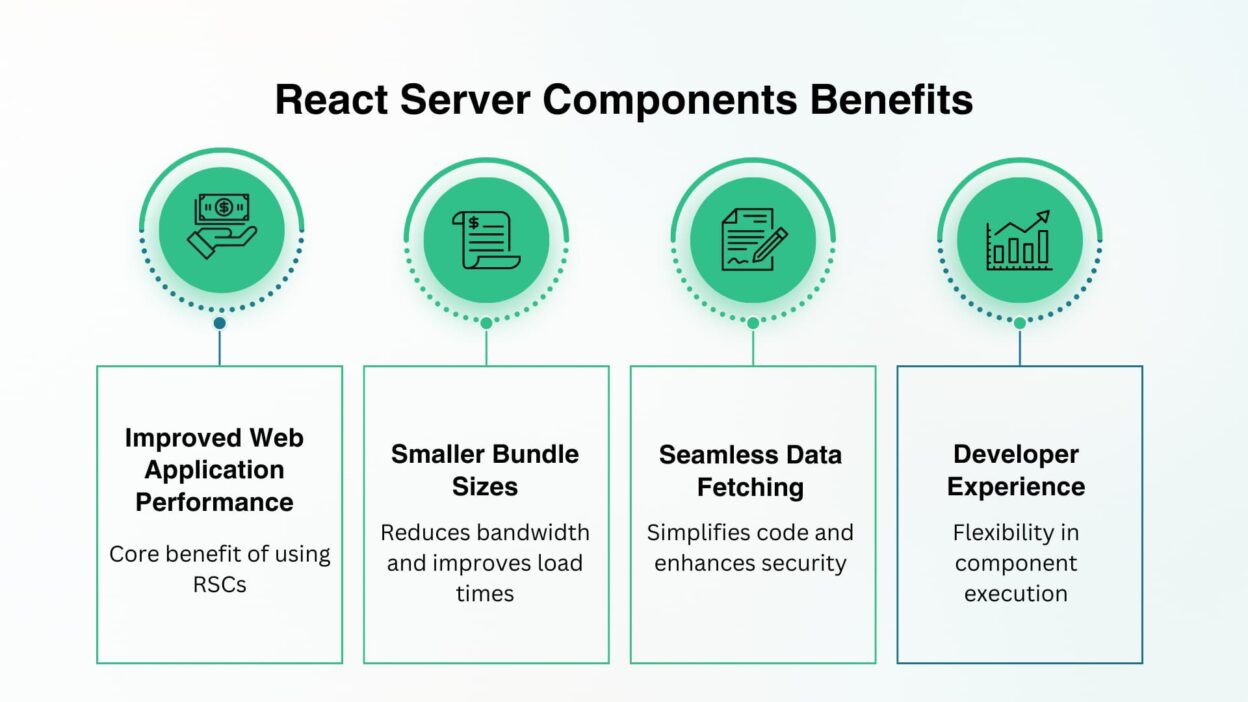
1. Performance at Scale
In 2025, web applications are more complex and data-heavy than ever. Traditional client-side rendering often results in large bundle sizes and slower load times. RSCs solve this by:
- Eliminating unnecessary JavaScript.
- Streaming only the rendered markup.
- Allowing partial hydration when client-side interactivity is required.
2. Seamless Data Fetching
With RSCs, data fetching happens directly on the server. Developers can call APIs, databases, or external services without exposing API keys to the client.
This leads to:
- Simplified code (no need for complex API calls in the client).
- More secure applications.
- Reduced over-fetching and under-fetching of data.
3. Smaller Bundle Sizes
In a typical React app, even static content must ship JavaScript. With RSCs, non-interactive components are excluded from the client bundle. This means:
- Smaller bundle sizes.
- Reduced bandwidth usage.
- Improved performance on mobile and low-powered devices.
4. Developer Experience
By mixing server and client components in the same React tree, developers can choose the right execution environment for each component. This flexibility improves maintainability while keeping the familiar React mental model.
Example:
- Use Server Components for static text, product listings, or blog posts.
- Use Client Components for interactive UI like dropdowns, modals, or carousels.
How React Server Components Compare
Here’s a comparison of Client Components, Server-Side Rendering (SSR), and React Server Components (RSCs):
| Feature | Client Components | SSR (Server-Side Rendering) | React Server Components |
| JavaScript Bundles | Large | Medium | Minimal (only where needed) |
| Data Fetching | Client-side APIs | Server + client hydration | Direct server APIs (secure) |
| Initial Load Speed | Slower | Faster than CSR | Fastest |
| Interactivity | Full | Full | Client + Server mix |
| SEO Benefits | Limited | Good | Excellent |
| Complexity | High (API mgmt) | Medium | Medium–Low |
Real-World Use Cases in 2025
- E-commerce Platforms
- Product catalogs rendered via RSCs → instant load.
- Checkout and cart logic remain client-side.
- Content-Heavy Websites (Blogs, News, Documentation)
- Articles, documentation pages, and static resources served as RSCs.
- Interactive widgets like comment sections handled by client components.
- Enterprise Dashboards
- Large datasets rendered on the server.
- Interactive filters and graphs on the client.
- AI-Powered Applications
- RSCs fetch AI responses directly from server APIs.
- Client only handles display and user interactivity.
How RSCs Fit Into Modern Frameworks
In 2025, frameworks like Next.js 15, Remix, and Astro are embracing RSCs as a core feature.
- Next.js App Router integrates RSCs natively, making it easy to build hybrid apps.
- Remix leverages server rendering but is experimenting with RSC-like optimizations.
- Astro uses partial hydration and now supports React Server Components for better performance.
Best Practices for Using React Server Components in 2025
- Keep Interactivity Client-Side
- Buttons, modals, and animations should remain client-driven.
- Server-Only for Data-Heavy Components
- Use RSCs for static or data-driven sections to reduce bundle size.
- Combine with Streaming
- Use streaming with Next.js or Node.js to deliver partial content faster.
- Optimize for SEO
- Ensure RSC-rendered content includes structured data for better Google indexing.
- Test Performance Metrics
- Use Lighthouse and Web Vitals to measure gains.
Common Pitfalls and Challenges
While RSCs are powerful, developers in 2025 still face challenges:
- Learning Curve: Understanding when to use server vs client components can be tricky.
- Tooling Support: Some libraries are not fully RSC-compatible yet.
Caching & State Management: Managing server and client states together requires careful planning. - Hosting Requirements: RSCs need server infrastructure (Node.js, Bun, Deno runtimes) which may increase costs compared to static hosting.
Conclusion
As of 2025, React Server Components represent a paradigm shift in web development. By reducing JavaScript bundles, streamlining data fetching, and improving SEO, RSCs empower developers to build faster, more efficient, and scalable applications.
For technical teams, adopting RSCs isn’t just about chasing a trend—it’s about aligning with the future of modern web performance. If you’re already working with React, exploring RSCs is no longer optional; it’s a competitive necessity.
Next Step: Start experimenting with RSCs in your Next.js 15 projects and measure the performance improvements firsthand.
FAQs
How do React Server Components differ from Next.js SSR?
RSCs don’t hydrate unnecessary JavaScript on the client, while SSR still sends a full JS bundle for hydration.
Are React Server Components production-ready in 2025?
Yes. With Next.js 15 and React 19, RSCs are stable and widely adopted in enterprise-level applications.
Can I migrate my existing React app to use RSCs?
Yes, migration is incremental. You can start by converting non-interactive parts of your app into server components.
Do RSCs replace Client Components?
No. They complement client components. Use RSCs for static, non-interactive UI and client components for dynamic functionality.