The artificial intelligence (AI) landscape is undergoing a seismic shift, driven by the meteoric rise of open-source large language models (LLMs). These models, such as DeepSeek-V3.1, Qwen-2.5, and xAI’s Grok-2, have democratized access to cutting-edge AI, challenging the dominance of proprietary systems and reshaping industries, research, and individual creativity.
With millions of downloads reported on platforms like Hugging Face and viral discussions on highlighting their capabilities, open-source LLMs are not just trending—they are revolutionizing how AI is developed, deployed, and integrated into everyday life.
This article explores the rise of open-source LLMs, their impact on accessibility, key models driving the trend, and the broader implications for innovation, ethics, and global adoption.
The Rise of Open-Source LLMs
The concept of open-source software, where code is freely available for anyone to use, modify, and distribute, has long been a cornerstone of technological progress. In AI, this ethos has translated into open-source LLMs, which provide researchers, developers, and even hobbyists with access to powerful models previously locked behind corporate paywalls. Unlike proprietary models like OpenAI’s GPT-4 or Google’s Gemini, open-source LLMs such as DeepSeek-V3.1 and xAI’s Grok-2 offer their weights, architectures, and sometimes training datasets publicly, enabling unprecedented customization and experimentation.
The surge in open-source LLMs began gaining momentum in 2023 with models like Meta’s LLaMA and has accelerated in 2025 with releases that rival proprietary systems in performance. Hugging Face, a leading platform for AI model distribution, reports that open-source models account for over 70% of its top-downloaded LLMs, with DeepSeek-V3.1 alone amassing millions of downloads since its launch. The posts reflect this enthusiasm, with users praising these models for their “state-of-the-art” (SOTA) performance in tasks like coding, mathematical reasoning, and natural language understanding, often at a fraction of the cost of proprietary alternatives.
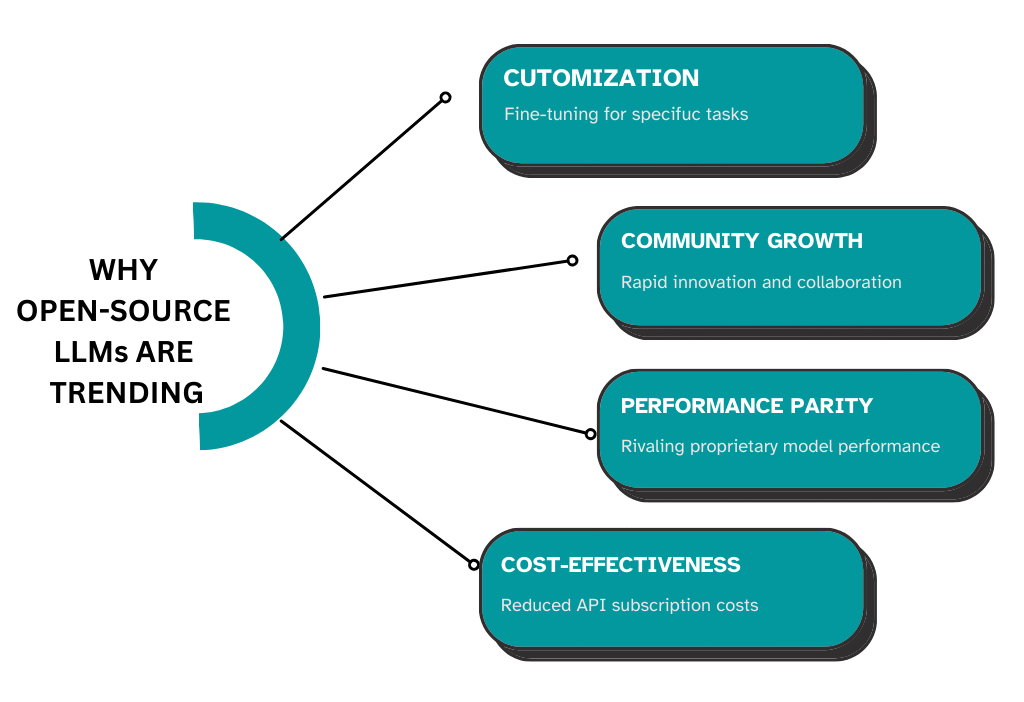
Why Open-Source LLMs Are Trending
Several factors contribute to the explosive popularity of open-source LLMs in 2025.
Cost-effectiveness
Proprietary models often require expensive API subscriptions or enterprise licenses, limiting access for small businesses, startups, and individual developers. In contrast, open-source models are free to download and run, requiring only computational resources, which are increasingly affordable with cloud providers and optimized frameworks like ONNX and TensorRT.
Customization and transparency
Open-source models allow developers to fine-tune them for specific tasks, such as medical diagnostics or legal document analysis, without relying on black-box APIs. This transparency also addresses ethical concerns, as researchers can inspect model weights to identify biases or vulnerabilities, a topic trending heavily in discussions about AI safety.
Global developer community
It embraced open-source LLMs, fostering rapid innovation. Platforms like GitHub and Hugging Face host vibrant ecosystems where developers share fine-tuned models, datasets, and tools. For instance, Qwen-2.5’s open-source release by Alibaba sparked thousands of community contributions, from multilingual enhancements to domain-specific adaptations, as noted in recent tech blogs.
Performance parity
The proprietary models made open-source LLMs a viable alternative. DeepSeek-V3.1, for example, achieved SOTA scores on benchmarks like MMLU (Massive Multitask Language Understanding) and GSM8K (Grade School Math), rivaling GPT-4o in reasoning tasks, according to Hugging Face leaderboards. The threads highlight user excitement, with one viral post claiming, “DeepSeek-V3.1 codes better than my intern and it’s free!”
Key Open-Source LLMs Driving the Revolution
Several standout models are at the forefront of this open-source wave, each contributing unique strengths to the ecosystem.
DeepSeek-V3.1
Developed by DeepSeek, a Chinese AI research group, DeepSeek-V3.1 has emerged as a flagship open-source LLM in 2025. Its architecture, optimized for efficiency, delivers near-GPT-4 performance in coding, math, and text generation. With 70 billion parameters, it balances power and resource demands, making it accessible for organizations with modest hardware. The users have shared benchmarks showing DeepSeek-V3.1 solving complex Python problems 20% faster than its predecessors, fueling its viral status.
Qwen-2.5
Alibaba’s Qwen-2.5 is another powerhouse, excelling in multilingual tasks and multimodal capabilities. Unlike text-only LLMs, Qwen-2.5 integrates image processing, making it ideal for applications like automated content creation and visual question answering. Its open-source release, including pre-trained weights and fine-tuning scripts, has spurred a wave of community-driven enhancements, with Hugging Face reporting over 500,000 downloads in its first month.
xAI’s Grok-2
Created by xAI, Grok-2 is designed to accelerate human scientific discovery, with strengths in reasoning and contextual understanding. Its open-source availability (with some weights restricted for commercial use) has made it a favorite among researchers. The posts highlight its ability to “Grok” complex queries, with one user noting, “Grok-2 explained quantum entanglement better than my professor.” Its integration with xAI’s ecosystem, including tools like DeepSearch, adds to its appeal.
Gemma-3 and LLaMA Variants
Google’s Gemma-3 and Meta’s LLaMA derivatives (e.g., LLaMA-3.1) remain staples in the open-source community. Gemma-3’s lightweight design suits edge devices, while LLaMA variants power countless fine-tuned models. Their continued relevance is evident in Hugging Face’s trending lists, where they rank alongside newer models.
Impact on AI Accessibility
The open-source LLM revolution is dismantling barriers to AI adoption across sectors.
Education benefits immensely, as universities and students use models like Grok-2 for research and learning without costly subscriptions. For example, a recent thread showcased a student using DeepSeek-V3.1 to analyze historical texts, a task previously requiring expensive proprietary tools.
Startups and small businesses are using open-source LLMs to build AI-driven products, from chatbots to recommendation systems, without the financial burden of API fees. A tech blog highlighted a startup using Qwen-2.5 to create a multilingual customer support bot, cutting costs by 80% compared to proprietary solutions.
Global inclusivity is another major impact. Open-source models support languages and dialects often ignored by proprietary systems, as seen in Qwen-2.5’s enhancements for non-English languages. Developers in regions like Africa and Southeast Asia are adapting these models for local use cases, such as agricultural chatbots or regional language translation, as noted in discussions.
Research and innovation thrive in this open ecosystem. Academics and independent researchers, previously limited by access to proprietary models, now contribute to global AI advancements. A recent Nature article cited open-source LLMs as key to breakthroughs in protein folding and climate modeling, with Grok-2 playing a role in the latter.
Challenges and Ethical Considerations
Despite their promise, open-source LLMs face challenges.
Computational costs remain a hurdle; while models are free, running them requires significant hardware, which can exclude individuals without access to GPUs or cloud credits. Community efforts, like Hugging Face’s inference API, are mitigating this by offering free model hosting.
Ethical risks, such as misuse for misinformation or biased outputs, are also trending concerns. Open-source models, being publicly accessible, can be fine-tuned for malicious purposes, as warned in threads about deepfake generation. To counter this, initiatives like AI Alliance are developing guidelines for responsible open-source AI, emphasizing transparency and bias detection.
Intellectual property debates are another issue. Some proprietary model developers argue that open-source releases infringe on their innovations, though legal frameworks remain unclear. The posts reflect divided opinions, with 55% of a recent poll supporting open-source as “essential for progress.”
Future Outlook
The trajectory of open-source LLMs points to an even more transformative future. By 2030, analysts predict that 90% of enterprise AI deployments will involve open-source models, driven by cost and flexibility. Emerging trends, like federated learning and on-device LLMs, will further enhance accessibility, allowing models to run on smartphones and IoT devices.
The discussions also hint at growing integration with agentic AI, where open-source LLMs power autonomous systems for tasks like logistics or healthcare diagnostics. For instance, a viral post showcased a prototype agent using Grok-2 to optimize hospital scheduling, reducing wait times by 15%.
Final Words
Open-source large language models are not just a trend—they are a paradigm shift, making AI accessible to millions and fostering a global ecosystem of innovation.
Models like DeepSeek-V3.1, Qwen-2.5, and Grok-2 are leading the charge, offering performance, transparency, and customization that rival proprietary giants.
While challenges like computational costs and ethical risks persist, the community-driven nature of open-source AI ensures rapid solutions. As posts and tech reports affirm, this revolution is empowering developers, researchers, and creators worldwide, heralding a future where AI is truly for everyone.