Global supply chains are the lifeblood of modern business. From the clothes we wear to the devices we use, products travel across multiple countries, suppliers, and regulatory environments before reaching us. Yet, the traditional supply chain is plagued with challenges: lack of transparency, inefficiencies, high costs, and vulnerabilities to fraud or disruption.
Enter blockchain. Once associated mainly with cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, blockchain has evolved into a powerful technology transforming industries—including supply chain management. In 2025, businesses are no longer asking if blockchain will impact supply chains, but how fast they need to adapt.
This article explores how blockchain is reshaping global supply chains, the opportunities it unlocks, the challenges it presents, and what it means for business leaders today.
1. Why Supply Chains Need Blockchain
Traditional supply chains often operate in silos. Different stakeholders—manufacturers, suppliers, logistics providers, distributors, and retailers—use separate systems. This leads to:
- Poor visibility: Companies often don’t know where materials come from or where bottlenecks exist.
- Fraud and counterfeiting: Fake products enter the market, especially in industries like pharmaceuticals, luxury goods, and electronics.
- Inefficiency: Manual paperwork and reconciliation across parties create delays and errors.
- Regulatory risks: Compliance with customs, labor laws, or sustainability reporting is cumbersome.
Blockchain addresses these pain points by offering a shared, immutable, and transparent ledger of transactions that all participants can trust.
2. Core Features of Blockchain That Power Supply Chains
1. Transparency
Blockchain creates a single source of truth. Every transaction—whether raw materials purchased, goods shipped, or payments made—is recorded and viewable across the network.
2. Traceability
With blockchain, businesses can track every step of a product’s journey, from origin to consumer. This is particularly valuable in food, pharmaceuticals, and ethically sourced products.
3. Security
Because records on a blockchain are tamper-proof, the risk of fraud or unauthorized changes is drastically reduced.
4. Automation with Smart Contracts
Blockchain enables smart contracts—self-executing agreements that trigger automatically when certain conditions are met. Example: releasing payment when goods arrive at a port.
3. Real-World Applications of Blockchain in Supply Chains
1. Food Safety and Traceability
Walmart, Carrefour, and other retailers use blockchain to trace food products from farm to shelf. For instance, Walmart reduced the time to trace mangoes in its supply chain from 7 days to just 2.2 seconds using blockchain.
2. Pharmaceutical Authenticity
Counterfeit drugs cost the global economy billions and endanger lives. Companies like Pfizer are leveraging blockchain to authenticate drugs and comply with regulations such as the U.S. Drug Supply Chain Security Act (DSCSA).
3. Luxury Goods Verification
Brands like LVMH and Prada are experimenting with blockchain to prove product authenticity and fight counterfeiting in luxury goods.
4. Logistics and Shipping
Maersk and IBM’s now-concluded project, TradeLens, showcased blockchain’s potential in digitizing shipping documents, customs clearance, and reducing paperwork. Though it shut down due to adoption challenges, it proved blockchain’s efficiency in reducing costs and delays.
4. Sustainable Sourcing
Consumers increasingly demand ethically and sustainably sourced products. Blockchain helps prove whether coffee is fair trade, diamonds are conflict-free, or clothing materials are environmentally friendly.
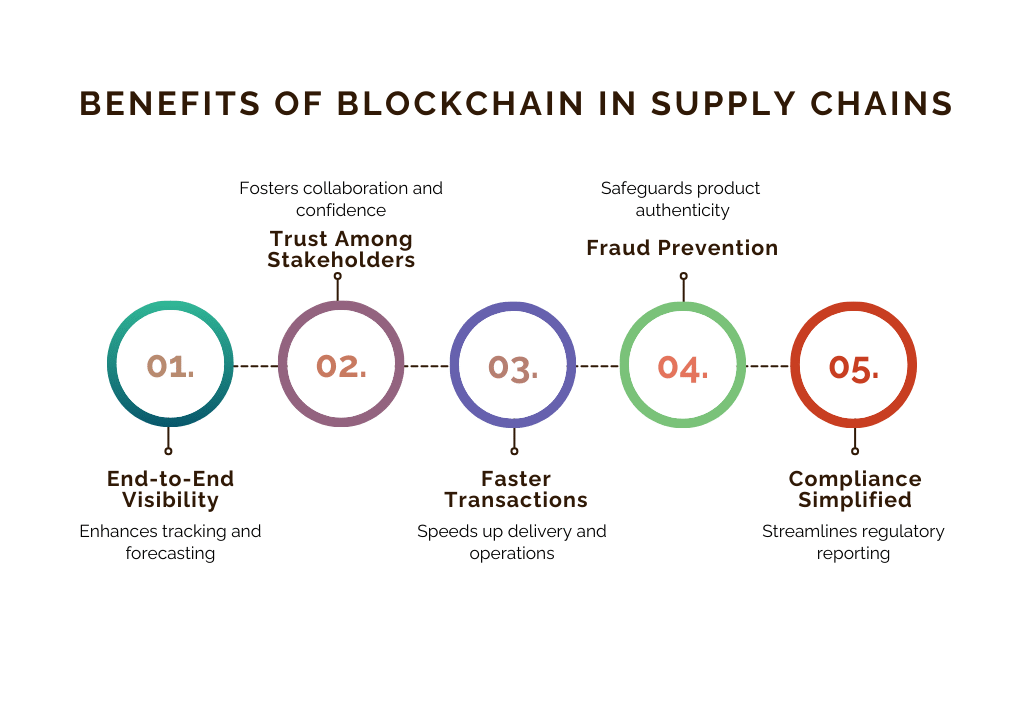
4. Benefits of Blockchain in Supply Chains
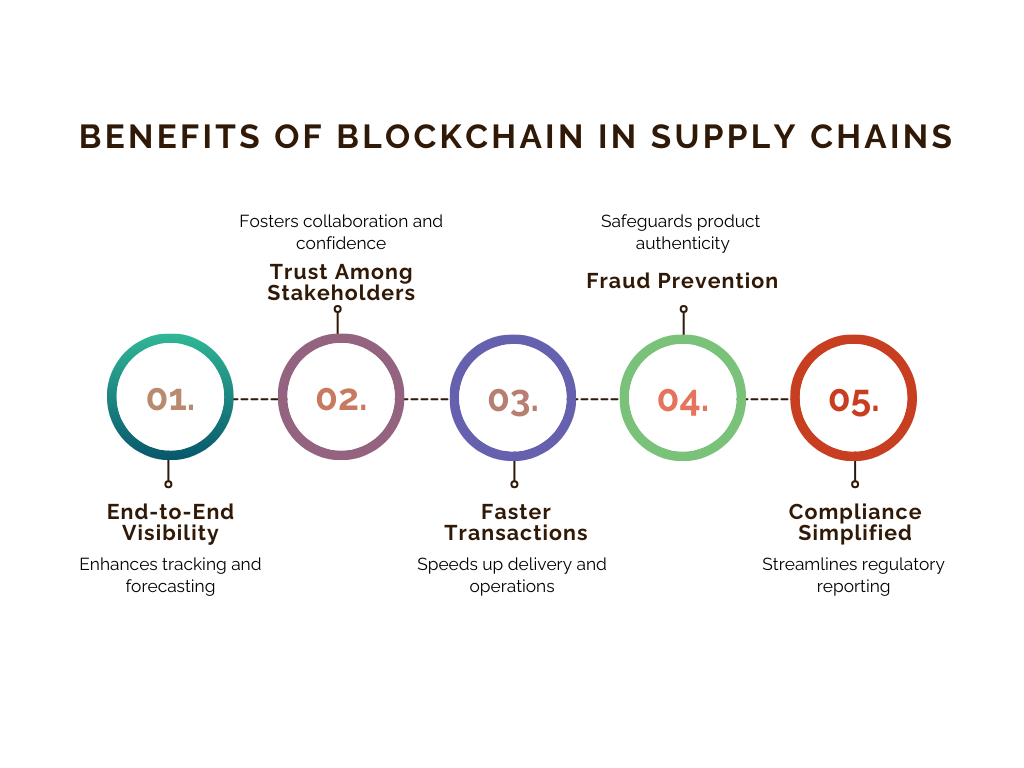
End-to-End Visibility
Blockchain creates a transparent record of product journeys, making it easy to track goods at every stage. This reduces blind spots, improves forecasting, and helps businesses respond quickly to disruptions.
Trust Among Stakeholders
Shared, tamper-proof data eliminates disputes and fosters collaboration across the supply chain. It builds confidence among suppliers, customers, and regulators.
Faster Transactions
Smart contracts and digital records cut delays caused by paperwork and manual approvals.
This speeds up delivery times and ensures smoother operations.
Fraud Prevention
Immutable blockchain records make counterfeiting and manipulation nearly impossible.
Industries like pharma and luxury goods benefit by safeguarding product authenticity.
Compliance Simplified
Regulatory reporting and audits become more straightforward with blockchain-based records.
It ensures companies meet safety, labor, and sustainability standards with less effort.
5. Challenges Holding Back Adoption
Scalability
Many blockchain networks struggle to handle the massive volume of global supply chain transactions. This creates performance issues when expanding beyond pilot programs.
Interoperability
Supply chains span multiple countries and systems, but blockchain platforms often operate in silos. Integrating different blockchains remains a major technical challenge.
High Implementation Costs
Deploying blockchain requires investment in technology, integration, and training.
Smaller businesses may find upfront costs difficult to justify.
Resistance to Change
Supply chain partners may be reluctant to share sensitive data or adopt new systems.
Cultural and organizational inertia slows down adoption.
Regulatory Uncertainty
Different regions have unclear or evolving rules around blockchain usage.
This creates risks for companies operating across borders.
6. Blockchain + AI + IoT: The Future of Supply Chains
The real power of blockchain emerges when it converges with other technologies:
- AI (Artificial Intelligence) – AI analyzes blockchain data to predict demand, optimize routes, and detect anomalies.
- IoT (Internet of Things) – Sensors on shipments (temperature, location, humidity) feed real-time data into blockchain for end-to-end visibility.
- 5G Connectivity – Enables seamless data transmission from IoT devices to blockchain networks worldwide.
7. Industries Leading the Way
Food & Agriculture
Blockchain ensures farm-to-fork transparency, helping track the origin and quality of produce.
It reduces food contamination risks and minimizes waste through faster recalls and better inventory management.
Pharma & Healthcare
Blockchain secures the authenticity of medicines and prevents counterfeit drugs from entering supply chains.It also improves compliance with strict health regulations, protecting both patients and providers.
Fashion & Retail
Luxury and fashion brands use blockchain to prove authenticity and ethical sourcing of materials. It strengthens consumer trust by providing verifiable sustainability and fair-trade credentials.
Automotive
The automotive industry uses blockchain to track parts across complex, global supply chains.
It helps prevent counterfeit components while ensuring safety, reliability, and regulatory compliance.
Energy
Blockchain verifies renewable energy certificates and carbon credits, boosting transparency in sustainability claims. It enables businesses and governments to monitor, trade, and optimize clean energy usage more efficiently.
8. The Strategic Value for Businesses
For tech business owners and CTOs, blockchain is not just a supply chain tool—it’s a strategic enabler. Here’s why:
- Competitive Advantage: Companies adopting blockchain can market their transparency and ethical sourcing.
- Risk Reduction: Real-time traceability helps mitigate disruptions.
- Customer Trust: Transparent supply chains strengthen brand loyalty.
- Financial Gains: Faster processes and reduced fraud mean cost savings and higher margins.
9. Steps for Businesses to Get Started
Identify Pain Points
Begin by mapping your supply chain to uncover inefficiencies, fraud risks, or blind spots.
Targeting specific problem areas ensures blockchain adoption solves real challenges instead of becoming just a buzzword.
Start with a Pilot
Launch a small-scale project, such as tracking one product line or shipment route.
This controlled approach helps test feasibility, measure benefits, and build internal confidence before full rollout.
Engage Stakeholders
Blockchain’s value multiplies when suppliers, logistics providers, and regulators are on board.
Collaborating early ensures smoother adoption, stronger trust, and shared responsibility for results.
Choose the Right Platform
Select between public, private, or consortium blockchains based on your industry and security needs. The right platform balances transparency, scalability, and compliance with your business goals.
Integrate with IoT & AI
Combine blockchain with IoT sensors and AI analytics to enhance traceability and predictive insights. This integration creates a smarter, more autonomous supply chain that adapts in real time.
Measure ROI
Track both financial savings and operational improvements to justify investment.
Metrics like reduced fraud, faster transactions, and improved customer trust highlight blockchain’s true impact.
Final Thoughts
In 2025, blockchain is no longer a futuristic experiment—it’s becoming a practical solution to some of the most pressing challenges in global supply chains. By bringing transparency, security, and efficiency, blockchain is helping businesses build supply chains that are not only more resilient but also more trusted.
For tech business leaders and CTOs, the question isn’t whether blockchain will impact supply chains, but how quickly they can adapt to stay ahead. Companies that embrace this shift will gain an edge in efficiency, compliance, and customer trust—while those that delay risk falling behind.
Blockchain is not just changing supply chains. It’s redefining the trust economy.